A Stationary series is one whose statistical properties such as mean, variance, covariance, and standard deviation do not vary with time, or these stats properties are not a function of time. In other words, stationarity in Time Series also means series without a Trend or Seasonal components.
- Constant mean
- Constant Variance
- Constant covariance
Visual Signs of Non-Stationarity 👀 - Trend: A clear upward or downward movement over time. The mean is not constant.
Seasonality: A pattern that repeats at regular intervals (e.g., yearly, monthly, weekly).
Varying Variance: The spread of the data points increases or decreases over time, making the series appear wider or narrower
- Seasonality can be observed in series (d), (h), and (i)
- The trend can be observed in series (a), (c), (e), (f), and (i)
- Series (b) and (g) are stationary
ADF Test: - Null Hypothesis (HO): Series is non-stationary - Alternate Hypothesis(HA): Series is stationary
Reject the null hypothesis if p-value < 0.05
KPSS Test - Null Hypothesis (HO): Series is trend stationary - Alternate Hypothesis(HA): Series is non-stationary
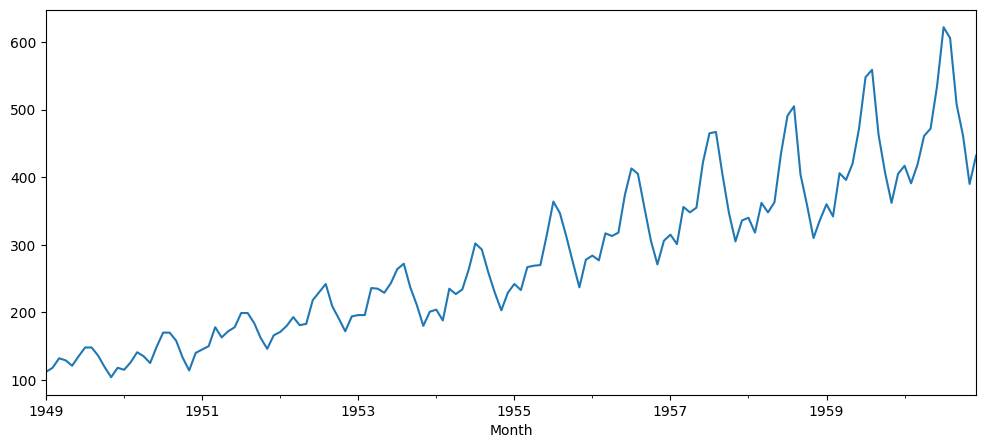
| Passengers | |
|---|---|
| Month | |
| 1949-01-01 | 112 |
| 1949-02-01 | 118 |
| 1949-03-01 | 132 |
| 1949-04-01 | 129 |
| 1949-05-01 | 121 |
| ... | ... |
| 1960-08-01 | 606 |
| 1960-09-01 | 508 |
| 1960-10-01 | 461 |
| 1960-11-01 | 390 |
| 1960-12-01 | 432 |
144 rows × 1 columns
| 0 | |
|---|---|
| Test Statistic | 0.815369 |
| p-value | 0.991880 |
| #Lags Used | 13.000000 |
| Number of Observations Used | 130.000000 |
| Critical Value (1%) | -3.481682 |
| Critical Value (5%) | -2.884042 |
| Critical Value (10%) | -2.578770 |
/tmp/ipython-input-752976516.py:1: InterpolationWarning: The test statistic is outside of the range of p-values available in the
look-up table. The actual p-value is smaller than the p-value returned.
kpsstest = kpss(df["Passengers"], regression='c', nlags="auto")| 0 | |
|---|---|
| Test Statistic | 1.651312 |
| p-value | 0.010000 |
| #Lags Used | 8.000000 |
| Critical Value (10%) | 0.347000 |
| Critical Value (5%) | 0.463000 |
| Critical Value (2.5%) | 0.574000 |
| Critical Value (1%) | 0.739000 |
The following are the possible outcomes of applying both tests.
- Case 1: Both tests conclude that the given series is stationary – The series is stationary
- Case 2: Both tests conclude that the given series is non-stationary The series is non-stationary
- Case 3: ADF concludes non-stationary, and KPSS concludes stationary The series is trend stationary. To make the series strictly stationary, we need to remove the trend in this case. Then we check the detrended series for stationarity.
- Case 4: ADF concludes stationary, and KPSS concludes non-stationary The series is difference stationary. Differencing is to be used to make series stationary. Then we check the differenced series for stationarity.
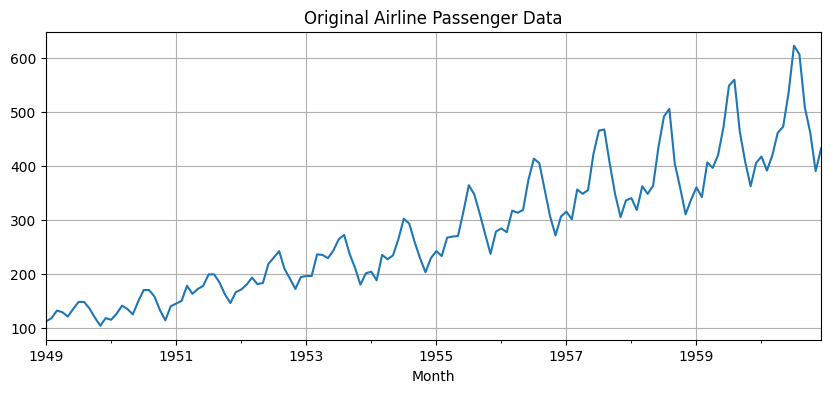
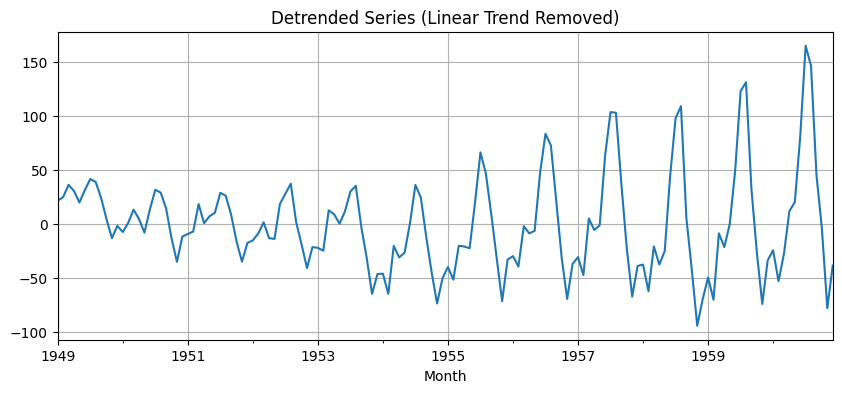
# Step 2: Stationarity Tests
# ADF Test
adf_orig_p = adfuller(df['Passengers'])[1]
adf_det_p = adfuller(df['detrended'])[1]
# KPSS Test
kpss_orig_p = kpss(df['Passengers'], regression='ct')[1] # trend + constant
kpss_det_p = kpss(df['detrended'], regression='c')[1] # constant only
# Step 3: Print Results
print("📊 Stationarity Test Results")
print(f"ADF (Original): p = {adf_orig_p:.4f} → {'Non-stationary' if adf_orig_p > 0.05 else 'Stationary'}")
print(f"KPSS (Original): p = {kpss_orig_p:.4f} → {'Non-stationary' if kpss_orig_p < 0.05 else 'Stationary'}")
print(f"ADF (Detrended): p = {adf_det_p:.4f} → {'Non-stationary' if adf_det_p > 0.05 else 'Stationary'}")
print(f"KPSS (Detrended): p = {kpss_det_p:.4f} → {'Non-stationary' if kpss_det_p < 0.05 else 'Stationary'}")
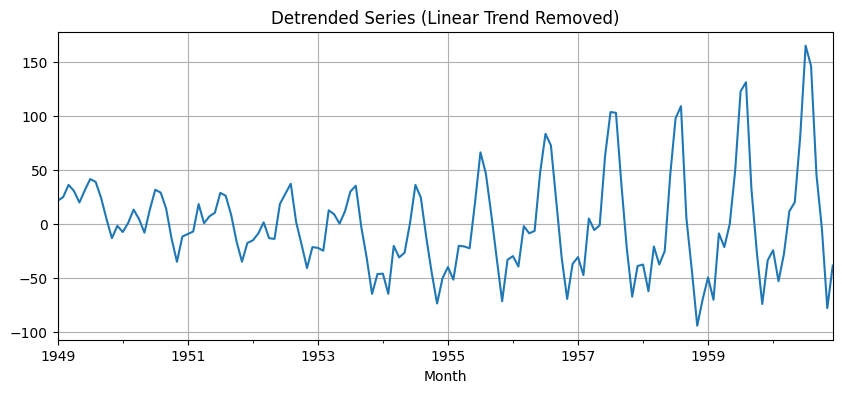
📊 Stationarity Test Results
ADF (Original): p = 0.9919 → Non-stationary
KPSS (Original): p = 0.1000 → Stationary
ADF (Detrended): p = 0.2437 → Non-stationary
KPSS (Detrended): p = 0.1000 → Stationary/tmp/ipython-input-2952525283.py:34: InterpolationWarning: The test statistic is outside of the range of p-values available in the
look-up table. The actual p-value is greater than the p-value returned.
kpss_orig_p = kpss(df['value'], regression='ct')[1] # trend + constant
/tmp/ipython-input-2952525283.py:35: InterpolationWarning: The test statistic is outside of the range of p-values available in the
look-up table. The actual p-value is greater than the p-value returned.
kpss_det_p = kpss(df['detrended'], regression='c')[1] # constant only